- Published 30 Jan 2023
- Last Modified 14 May 2024
- 10 min
A Complete Guide to Heat Shrink Tubing
We explain all about heat shrink tubing, including the different types, sizes, materials, and certifications.

What is Heat Shrink Tubing?
Heat shrink tubing is a versatile plastic layer that electricians, engineers, and similar professionals can apply to cabling and components for several purposes.
What Is Heat Shrink Tubing Used For?
- Electrical insulation - for example, to repair a damaged or exposed length of wire.
- Protection – from dust, chemicals, moisture or abrasion.
- Reinforcement – relieving the strain applied by cables held at tension.
- Bundling multiple wires into a single unit.
- Identification – the wide range of available colours allows for easy coding.
They are also known as heat shrink sleeves, in particular when used with cables.
The name refers to the fact that the tubing is designed to shrink into place and become rigid when heat is applied, providing a durable, protective coating.
Given the range of possible uses, heat shrink tubing is available in a variety of materials, sizes and colours. Some also come with a silicone adhesive liner to help the tubing stay in place once applied.
Watch out for the ‘shrink ratio’ – the relationship between the original size of the heat shrink tube and its shrunken form following application. This is usually either 2:1 or 3:1, with higher numbers indicating a greater ratio and therefore a tighter fit. For example, tubing with a 2:1 ratio will shrink to half its size and a 3:1 ratio indicates shrinkage to one-third the full size.
How to Use Heat Shrink Tubing Safely
It is important when using heat shrink tubing to proceed with caution and observe basic safety measures to avoid accidents or injuries. Here’s how to use heat shrink tubing:
- Choose the right size tubing with the correct shrink ratio to ensure a snug fit after shrinking. Ensure it covers the wire or components adequately across both breadth and length.
- Check the tubing's expandability to accommodate any potential size changes of the components. Follow recommended heating temperatures to prevent uneven application or melting.
- Cut a suitable length of tubing and slide it over the target components. Heat the tubing using a handheld heat gun or a heat shrink oven for precise application.
- When using a heat gun, move it back and forth across the tubing to evenly shrink it and avoid burns. Heat until the wrap is tightly secured.
Common Heat Shrink Tubing Materials
Heat shrink tubing works thanks to the responsiveness of the multiple materials used to make the product. Each has different strengths and properties.
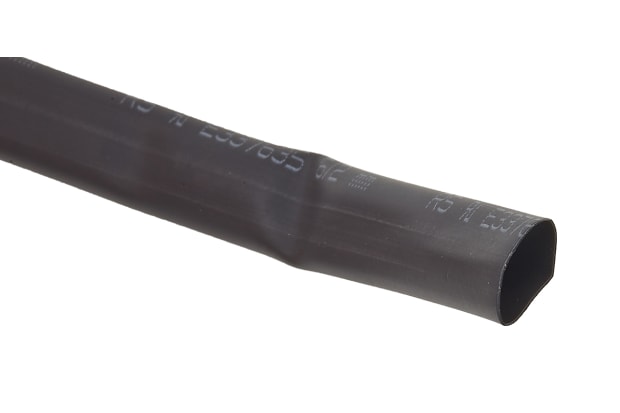

Polyolefin Heat Shrink Tubing
The synthetic polymer polyolefin is the most widely used heat shrink tubing material due to its resistance to high temperatures and chemical contamination.
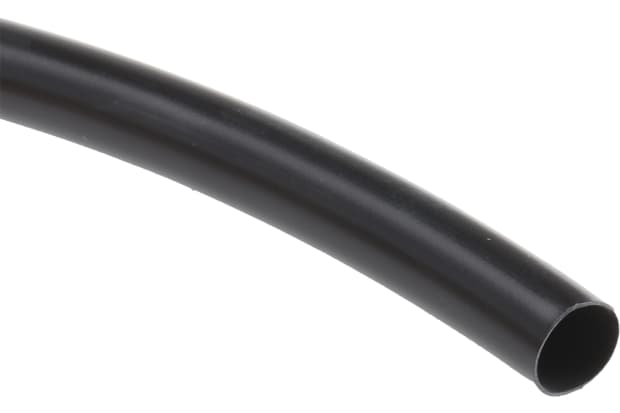

PVC Heat Shrink Tubing
Polyvinyl chloride or PVC is another widely used material in heat shrink tubing. It is versatile and provides a smooth surface.
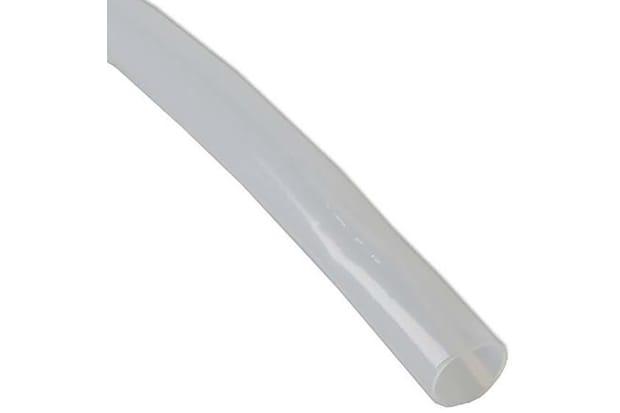

PTFE Heat Shrink Tubing
Polytetrafluoroethylene or PTFE is best known under the brand name Teflon®. When used in heat shrink tubing, this synthetic compound is highly resistant to chemicals and has an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, meaning that substances will slide off it very easily.
FEP Heat Shrink Tubing
Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) heat shrink tubing is highly resistant to chemical spillage, making it a good choice for sealant applications. It shrinks at a lower temperature than PTFE.
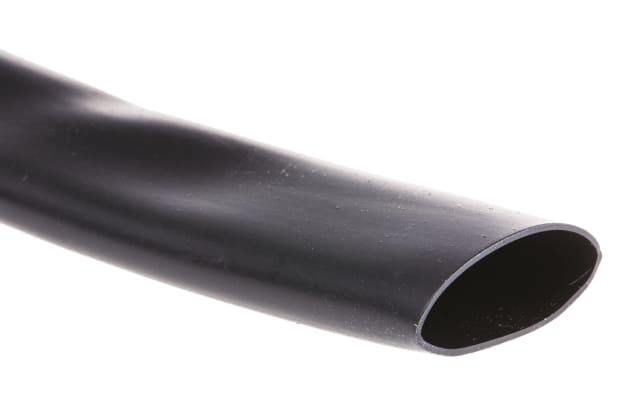

Elastomeric Heat Shrink Tubing
Elastomeric heat shrink tubing is noted for its flexibility as well as its resistance to abrasion and hazardous liquids like diesel fuel and hydraulic fluid. It is widely used in industrial environments to protect cabling.
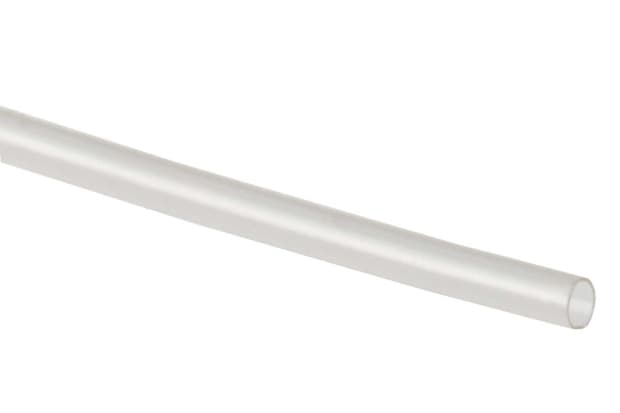

PVDF Heat Shrink Tubing
Polyvinylidene fluoride or PVDF heat shrink tubing is noted for its high level of resistance to flame, corrosive chemicals and industrial fuels. It is very robust and will not perforate easily.
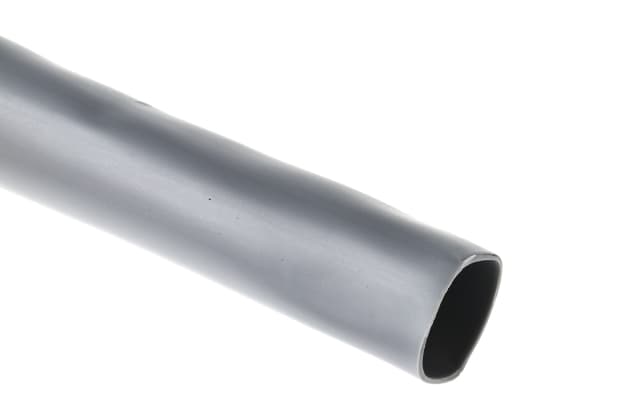

Silicone Heat Shrink Tubing
Silicone heat shrink tubing is noted for its flexibility and resilience when exposed to very high or very low temperatures. It is an excellent choice for insulation heating elements and bundling fibre optic cables. It is also widely used in medical environments because it withstands sterilisation conditions well.
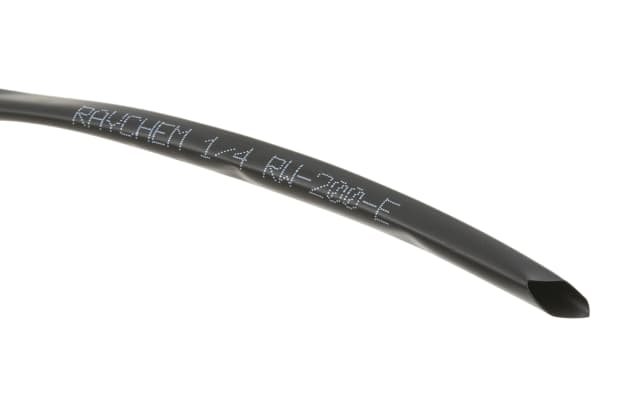

Viton Heat Shrink Tubing
Viton heat shrink tubing is made from fluoroelastomer, a type of synthetic rubber. It is resistant to high temperatures and remains flexible even at low temperatures. It forms an effective seal against oils, fuels and lubricants of various kinds.
Types of Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing is available in two basic types, single or dual wall, also known as thin or double wall.
Single or thin wall tubing is reliable and physically robust. It is a good choice when electrical insulation or protection against abrasion and strain is required.
By contrast, double or dual wall tubing is a better choice in situations where protection from corrosion or a firm seal is the primary aim. An additional adhesive layer within the tubing provides protection against moisture.
Heat Shrink Accessories
Here are some of the most commonly used heat shrink products and accessories:
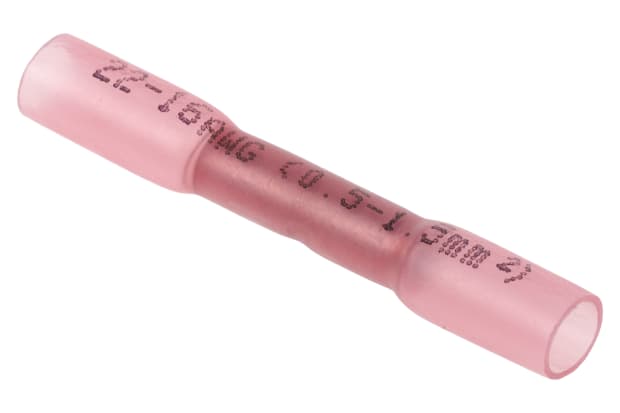

Heat Shrink Connectors
Heat shrink connectors or splices are a form of tubing used to join cabling together or to connect it to power outlets. They are available in various sizes and colours. Typically made from versatile materials like polyolefin, they usually feature a dual wall design, with a shrinkable outer layer and an inner which will melt into place when heat is applied to create a strong, watertight seal.

Heat Shrink Wrap
As the name suggests, heat shrink wrap is a variant of heat shrink tubing made to wrap around cabling during repair and splicing operations. Typically it has a shrink ratio of 3:1 and provides a firm a seal resistant to moisture, chemicals and fungal contamination.
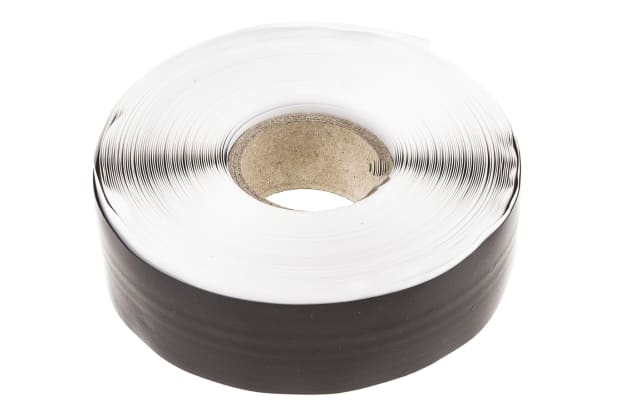

Heat Shrink Tape
Heat shrink tape works on similar principles to tubing and is typically used in conjunction with it for insulating seals and enclosures.
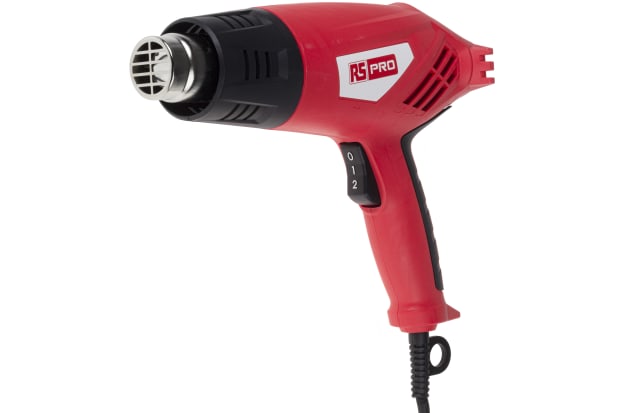

Heat Guns
Electric heat shrink guns are the principal method of applying heat to tubing, wrap and tape. These versatile appliances are lightweight and available with both single and double handles.
Related Uses
- Stripping Paint
- Thawing Pipes
- Removing Decals
Heat Shrink Products in Action
Take a look at this handy video to learn more about the various uses and properties of heat shrink. Additionally, make the most of the opportunity to see some heat shrink products from TE Connectivity in action!
What Size Heat Shrink Tubing Do You Need?
Determining what size heat shrink tubing you will need begins with the diameter of the materials to be covered.
- Measure the widest part of the cabling or components to be covered.
- Select tubing that is approximately 20-30% larger than the measurement taken in step one.
- Consider the shrink ratio of the tubing (e.g., 2:1 or 3:1) and the thickness of its walls.
- Take note of the 'inside diameter' (ID) of the tubing after shrinkage and its 'expanded inside diameter' (expanded ID) before shrinkage, typically displayed on the labelling.
- Account for the tubing's length, which decreases by five to ten percent when shrunk, to ensure full coverage.
What Size Heat Shrink Tubing Do You Need?
- 5mm tubing with a .198-inch diameter is the recommended heat shrink tubing size for 12-gauge wire.
- The recommended heat shrink tubing size for 14-gauge wire is the same as that for 12 - 5mm, with a .198-inch diameter.
- For 16-gauge wire, 3mm heat shrink tubing with a 2:1 shrink ratio and a .118-inch diameter is recommended.
- The recommended heat shrink tubing size for 18-gauge wire is the same as that for 16-gauge wire: 3mm with a 2:1 shrink ratio and a .118-inch diameter.
Heat Shrink Standards and Certificates
These are the principle standards and certificates for heat shrink tubing:
UL224-2010
UL224-2010 specifies requirements for round insulating tubing made from polymers with heat-setting, heat-responsive and elastic properties.
SAE AS23053
SAE AS23053 sets out requirements for electrical insulating sleeving that will shrink to a predetermined size when heat is applied.
ASTM D 2671
ASTM D 2671 specifies standard methods of testing heat shrink tubing intended for use with electrical cabling.
ASTM D3150
ASTM D3150 is a specification that applies to heat shrink made from PVC when used for electrical insulation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Top Heat Shrink Brands
TE Connectivity
TE Connectivity offers a wide selection of heat shrink tubing designed to provide durable and reliable insulation solutions. Their heat shrink products are known for their high quality and versatility, catering to various industrial and commercial applications. Browse TE Connectivity's range of heat shrink tubing for your insulation needs.
RS PRO
RS PRO provides a comprehensive range of heat shrink products designed to meet industry standards and specifications. With a focus on quality and performance, RS PRO's heat shrink tubing offers reliable insulation and protection for electrical and mechanical components. Explore RS PRO's full range of heat shrink products to find the right solution for your application.
3M
3M is a trusted name in the industry, known for its innovative solutions and high-quality products. Their heat shrink tubing products and accessories are designed to provide excellent insulation and protection for wires, cables, and other components. Browse 3M's extensive range of heat shrink tubing to find the perfect solution for your needs.
HellermannTyton
HellermannTyton offers a comprehensive range of heat shrink products and accessories designed to meet the demanding requirements of various applications. With a focus on durability and performance, HellermannTyton's heat shrink tubing provides reliable insulation and protection for wires and cables. Explore HellermannTyton's full range of heat shrink products to find the right solution for your project.
