- Automation & Control Gear
- Cables & Wires
- Enclosures & Server Racks
- Fuses & Circuit Breakers
- HVAC, Fans & Thermal Management
- Lighting
- Relays & Signal Conditioning
- Switches
- Batteries & Chargers
- Connectors
- Displays & Optoelectronics
- ESD Control, Cleanroom & PCB Prototyping
- Passive Components
- Power Supplies & Transformers
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ROCK, STEM Education & Development Tools
- Semiconductors
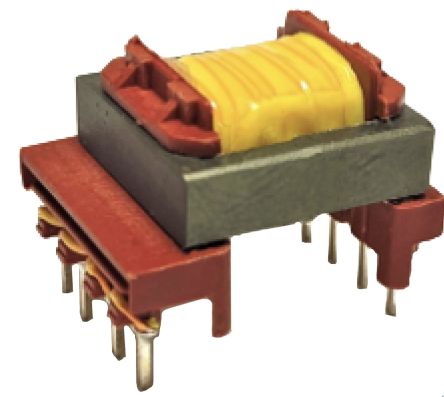
SMPS Transformers
SMPS Transformers carry out efficient power transfer when used in switch mode power supplies for industrial and commercial systems. The main reason they are preferred is their capability of providing a regulated output voltage to electrical networks that enable them to function properly.
However, understanding SMPS transformers can be a daunting task, especially for those who are new to the topic. But don't worry - with the right knowledge, you can get a good grasp on the different functions and components of SMPS transformers.
In this post, we'll take a look at what they are and how they work, so that you can make the most of your SMPS transformer.
SMPS Transformers
A switch mode power supply is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to efficiently convert electrical power.
On the other hand, switch mode power supply (SMPS) transformers are a highly efficient form of transformer, which can be found in devices such as computer systems. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a DC or AC source (which is often mains power) to DC loads, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics.
Due to its more efficient conversion and higher-quality voltage regulation, it has largely replaced older types of electronic transformers since the early 1980s.
They come in a variety of shapes and sizes and can offer unique features for different applications. Aside from being smaller and lighter, they have also improved durability, which makes them more suitable for portable electronic devices such as laptops, tablets, smartphones and digital cameras.
The SMPS transformer has 2 main components:
- an AC/DC rectifier and 2) DC/AC inverter. The AC/DC rectifier converts incoming AC voltage into DC voltage
How do switch-mode power supply (SMPS) transformers work?
Any switched-mode power supply that gets its power from an AC power line (also known as an 'off-line' converter) requires a transformer for galvanic isolation, which prevents current flow. Some DC-to-DC converters may also include a transformer.
SMPS transformers run at high frequencies. Most of the cost savings (as well as space savings) in off-line power supplies result from the smaller size of the high-frequency transformer.
Some SMPS transformers even have multiple outputs to provide greater flexibility for the application Thus, SMPS transformers are designed for power supplies that require a regulated output voltage with the capability to transfer large amounts of current.
SMPS Flyback Transformer
In switched-mode power supply (SMPS) circuits, flyback transformers are also called line output transformers or coupled inductors. In a circuit, it transfers energy by switching a primary winding on and off at a high frequency between a primary and secondary winding.
Flyback transformers convert voltages and currents in SMPS circuits. LCD displays, CRT displays, and other electronics that require high voltages or currents benefit greatly from isolated power.
Main Applications of SMPS Transformers
Their applications include low-noise switching power supplies for high-frequency circuits in consumer electronics, medical equipment such as pacemakers, automated industrial systems like robotics and other imaging systems.
They use the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer energy from one circuit to another, usually between a power source and a load. SMPS transformers are also designed to help reduce standby power consumption, making them great for energy-saving applications