- Published 6 Feb 2023
- Last Modified 25 Apr 2024
- 8 min
Heat Sink Buying Guide
Discover more about heatsinks, including why they're important and how to choose the best heatsink for your setup.

This guide is designed to give you a better understanding of what heat sinks do, how they’re fitted, and why they work as effectively as they do. If you’re trying to work out the most suitable heat sink for your setup, the information below should give you a clearer idea of the best heat sink to buy.
What is a Heat Sink?
Heat sinks are essential cooling devices widely used in electronics and machinery to dissipate heat generated during operation. They help components run efficiently and extend their lifespan by transferring heat away from the source. Heat sinks prevent overheating, which can lead to system failures or damage. In practice, the term ‘heat sink’ typically refers to various kinds ofelectronic cooling, where it might also be referred to as a heat spreader or simply a cooler. Coolers of this type are a form of radiator because they radiate the heat they collect out into the atmosphere and away from the source. While heat sinks come in various types and designs, they all serve the same purpose of cooling critical components.
Different Types of Heat Sink Materials
Heat sinks, typically made from metals like copper or aluminium, come in various designs such as the common 'fin' layout or alternative versions with pins or stamping techniques to enhance surface area and heat transfer rates. Most heat sinks are passive, naturally conducting heat away from the source when in direct contact with the component. However, active heat sinks, which incorporate powered fans for improved dissipation, are also available. For a comparison of widely used heat sink types, refer to the following sections.
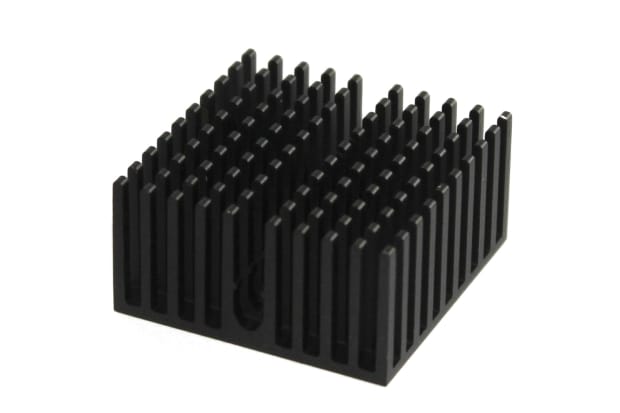

Passive Heat Sinks
Passive heat sinks, unlike their active counterparts, rely solely on direct contact with a component to disperse generated heat into the surrounding air. Due to this independent operation, they are typically larger and feature a finned or pin layout to maximise surface area for efficient heat transfer. These heat sinks, such as aluminium variants, are commonly employed in lower-power electronics or machinery where active cooling is unnecessary. They serve as cost-effective thermal transfer solutions, particularly for large components where active cooling is impractical but require ample clearance around the attached part.
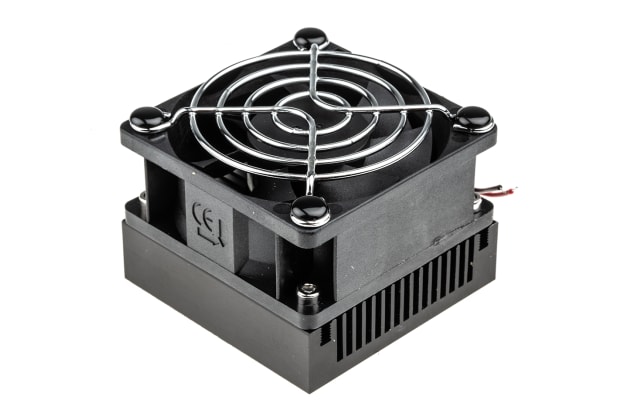

Active Heat Sinks
Active heat sinks, powered by fans, water pumps, or other processes, enhance cooling capacity and accelerate heat transfer rates, especially in computers and electronic systems. These coolers often draw power from the PC's internal supply. Common active cooling heat sinks employ fans mounted above or alongside the heat fin stack, circulating fresh air across the metal cooler for efficient thermal dissipation. Some setups feature integrated fans, known as HSFs.
Advanced active heat sinks may utilise liquid cooling, such as closed-loop coolers (CLCs). In CLCs, a pump circulates water or coolant through tubes, absorbing heat from a component via a contact plate before transferring it to a radiator for dissipation. Active cooling heat sinks function as a crucial temperature control system in electronics, safeguarding chips, LEDs, and ICs from overheating, particularly in computers, where CPUs and graphics cards can generate significant heat under load.
Inadequate cooling can lead to physical circuit damage or thermal throttling, where systems restrict component power to prevent heat buildup.
Copper Heat Sinks
Copper is frequently used as the core heat sink material for a wide range of designs due to its impressive heat transfer qualities. It’s an excellent thermal conductor, helping to draw heat quickly and efficiently away from the device or circuit you’re trying to cool. On the downside, copper heatsinks are typically more expensive (and up to three times heavier) than popular alternatives, such as aluminium.
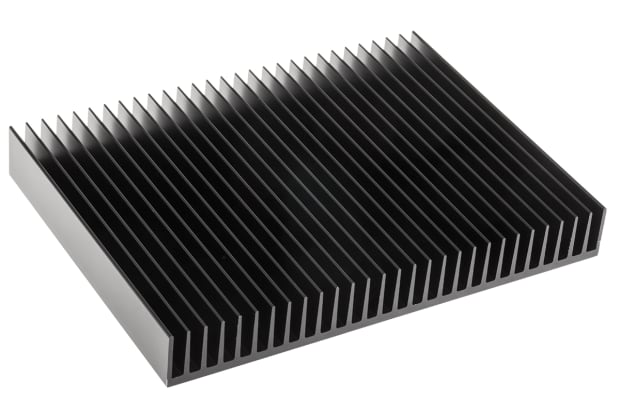

Aluminium Heat Sinks
Aluminium heat sinks, while not as efficient as copper in conducting heat, offer advantages in terms of weight, cost, and structural robustness, especially when constructed from thin sheets of extruded aluminium. They often feature a design with thin metal fins allowing heat to rise, as detailed below. Certain heat sink types, like bonded fin versions, may combine copper and aluminium, with one metal typically used for the base or contact plate (often copper) and the other for the fins.
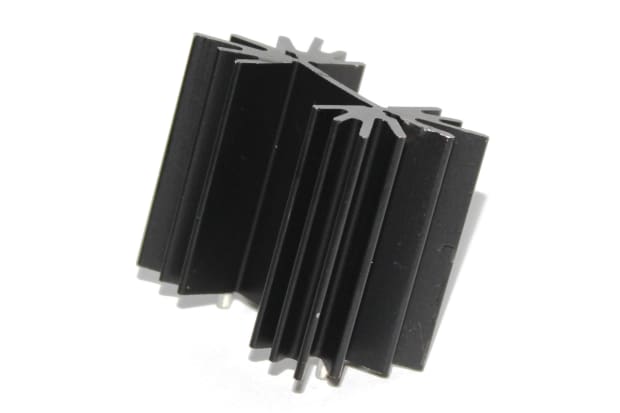

Finned Heat Sinks
Finned heat sinks are crafted from a solid metal block sliced into thin plates, increasing surface area for optimal heat transfer from the attached component. Various manufacturing processes are employed, including die-casting for mass production and CNC milling for higher quality, albeit lower volume, outputs. While die-cast models dominate high-volume sales due to their affordability, CNC-milled variants offer superior quality at a higher cost.
Pinned Heat Sinks
Pinned heat sinks, also known as pin-fin coolers, offer an alternative design to flat-fin heat sinks. These coolers feature a core block with pins or rods extending from its base, varying in shape from cylindrical to elliptical or square. While they boast a larger surface area than finned heat sinks, they may not always provide a substantial performance boost in typical applications, resulting in their less frequent use than fin models.
Heat Sink Manufacturing Types
As noted above, there is a wide variety of constructions, designs and manufacturing techniques used in making heatsinks for computers, motherboards and other devices. Common options include:
- Extruded heat sinks - the metal is simply forced into the required shape, extremely common in a wide range of applications.
- Forged heat sinks - relies on a die or mould to set the metal in the form needed, often cheaper for mass production.
- Bonded heat sinks - fins are individually attached to the base in a dense array, ideal for bespoke or space-limited applications.
- Stamped heat sinks - among the cheapest to mass-produce but generally less powerful and effective as coolers.
- **CNC machined heat sinks **- often among the more expensive options as the metal is precision-cut from a solid block, meaning much more material goes to waste.
- Skived or zipper fin heat sinks - a highly effective (and, again, typically more expensive) manufacturing process, using a dedicated machine to cut the fins and then push them up into position; identified by a slight curve at the fin base.
Most of these techniques offer alternate ways of achieving the classic finned or pinned heatsink layout. Typically, the choice will come down to striking the best balance for an individual supplier between quality, performance, cost, and sales volume.
What Can Heat Sinks Be Used for?
We’ve already touched on the importance of heatsinks for cooling vital PC components such as CPUs and GPUs. Some other examples of everyday heat sink uses include:
- Motherboard heatsinks
- Solid-state and relayheat sinks
- Power transistor heat sink
- PCB heat sinks
- External/internal laptop heatsinks
- Heat sinks for amplifiers
How to Choose the Right Heat Sink Types
When asking yourself ‘What type of heat sink should I buy?’, the answer will almost always come down to the specifics of your setup and cooling needs. Identifying some basic details about your intended application is the first step in knowing how to choose heat sinks.
Key considerations for the best choice of heat sink include:
- What sort of power draw will the component in question be using? This is often referred to as the TDP (thermal design power, or thermal design profile). TDP is often used as a basic indication of a component’s power consumption, especially with CPUs (processors) and GPUs (video cards). TDP ratings specify the maximum heat a component can use in watts. It’s typically a good indicator of how hot a particular part has the potential to get under load.
- How cool the component ideally needs to be kept in order to perform optimally?
- How much space is available to install a cooler, heat spreader, or heat sink - they’re available in a wide variety of sizes, from tiny module heat sinks to much larger installations.
- Which type of heat sink design or layout will give you the best thermal performance for your system specs?
- Whether you need an active heat sink or a passive radiator.
- How much you’re willing to spend on a cooler?
How Do You Fit a Heat Sink?
To fit a heat sink, attach the base plate tightly to the component using manual clamping or screw-down assembly. Various mounting accessories like spring clips, spring mount rivets, screws, and adhesive tapes are available. Applythermal paste between the component and the heat plate to enhance thermal transfer and fill in small gaps. Thermal paste improves cooling performance but may require periodic reapplication as it can dry and crack over time.
Heat Sinks by Brand
There are many trusted heat sink manufacturers. Some specialise in electronics and PC radiator models, while others are more commonly associated with industrial design and machine cooling.
The content below explores some of the popular heatsink brands, their applications and benefits.
Aavid heat sinks
Main Benefits:
- A comprehensive range of heat sinks
- Experts in a wide range of cooling solutions
Application:
- Perfect for a wide range of applications
Fischer heat sinks
Main Benefits:
- Experts in smaller heat sinks
- Extensive range available
Application:
- Many versions perfect for IC processors
RS PRO heat sinks
Main Benefits:
- Trusted brand
- Conforms to all the latest standards
Application:
- Ideal for a wide range of applications
Malico heat sinks
Main Benefits:
- High-quality product finishes
- Heat sinks designed to suit a range of performance levels
Application:
- Offer a range of heat sinks for different applications
Typical Applications of a Heat Sink
You can find some typical applications of the various types of heat sink materials in the table below.

FAQs
Popular Heat Sink Brands
AAVID THERMALLOY
AAVID THERMALLOY is renowned for its comprehensive range of high-quality heat sinks designed for various applications. With expertise in thermal management solutions,
AAVID THERMALLOY offers efficient cooling solutions for electronics and machinery.
Fischer Elektronik
Fischer Elektronik specialises in smaller heat sinks, offering an extensive range of products tailored to IC processors and other compact applications. Known for their reliability and performance, Fischer Elektronik heat sinks are trusted by professionals worldwide.